During the last decade, cloud storage technologies have emerged significantly, due to an expansion of huge amount of unstructured data. Cloud storage services is a distribution technique where the data are stored in a relational pool, these storage services can be accessed via a cloud computing services, an application programming interface (API), or applications that uses the API.
Every IT decision-makers today should know about the differences between the types of storage services object storage vs. block storage; in this article, we will highlight the main differences between cloud storage types and when to adopt each one of them.
Types of cloud storage for enterprises
Block storage
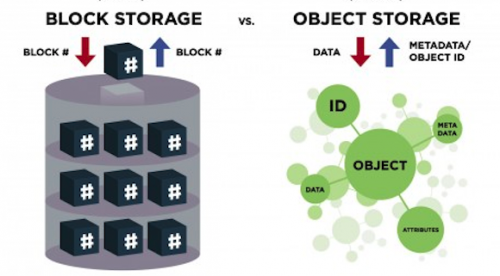
Block storage is the simplest and oldest type of data storage and most commonly used, in the block storage architecture, data is stored in as fixed-sized chunks called blocks or physical record, the application makes calls to find the exact block with the associated address. This address contains the metadata that been assigned to the block.
Block storage for a long time has been the best option for large businesses for its efficiency, speed and low latency, and flexibility. In addition, the storage devices can be easily removed and transferred, and the underlying architecture model behind it is famous and reliable, making it an ideal fit for applications that require high performance, such as transactional or database applications.
It is also significant to consider the limitations that block storage have. These include limited scalability and high latency, which can happen when the application has a higher distance from storage devices. Moreover, block storage can be expensive and complicated to maintain and optimize. For the above advantages and limitations, we can say that block storage is well designed for a variety of use cases that require consistent I/O performance and low latency connectivity such as relational databases, RAID volumes, and mission-critical applications like SAP, Oracle, Microsoft SharePoint, and Microsoft Exchange.
Object storage
Object storage is a new storage technology compared to block storage. It was created to manage the massive amount of unstructured data, for example, images, videos, text files and documents, social media data, surveillance imagery. Each object includes the data, a variable amount of metadata, and a unique identifier.

Object storage requires a simple HTTP based RESTful API calls such as POST, GET and PUT to access and manage the data, which is utilized by developers in most programming languages nowadays. Object storage is cost effective because the storage can run on commodity hardware, you can only pay per usage and can be conveniently scalable, making it an excellent storage choice for public clouds.
There are some disadvantages as well with object storage, objects are immutable, and it needs to be written completely at once. Also, storing of information doesn’t function well with conventional repositories and databases, as creating objects is a slow process and developing an app to use an object storage APIs is not as easy as using file storage.
The object storage is well suited for many use cases. For example, it is well suited in applications that uses large volumes of unstructured data, which are rarely modified. Object storage is also a good fit for backup and archiving data, as well as for large-scale applications uses advanced data analytics.
Making the object storage vs. block storage choice
Both objects, block storages has their advantages and disadvantages, with each use case suites a certain type of storage. You may not be using object storage to support your relational databases, but you may be using it to help your corporate web applications or large data analytics projects. The table below shows the main differences between these types of storage:
| Storage | Block | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Operating system | API’s |
| Type of data | Structured | Unstructured |
| Speed | Very fast | Fast |
| Multi access | No (volume attached to a single VM) | Yes (can be accessed by multiple VMs) |
| Cost | $$ | $ |
| Use cases | Operating systems, Data bases | Backup, Media, archive, document |
Luckily, the decision of adopting object and block storage is becoming much smoother as the cloud service providers today offer multiple data storage solutions, understanding the use cases and costs related with each segment will help you get the best out of the investment.
Available cloud storage offerings at Bluvalt Cloud
- vDC - Bluvalt provides a highly-capable computing resources that can be adjusted on-demand over the internet. To let you benefit from the top-notch techs with minimal costs.
- Object Storage - Bluvalt object storage is scalable, highly available and secure.This means customers of all sizes can use it to store and protect any amount of data.